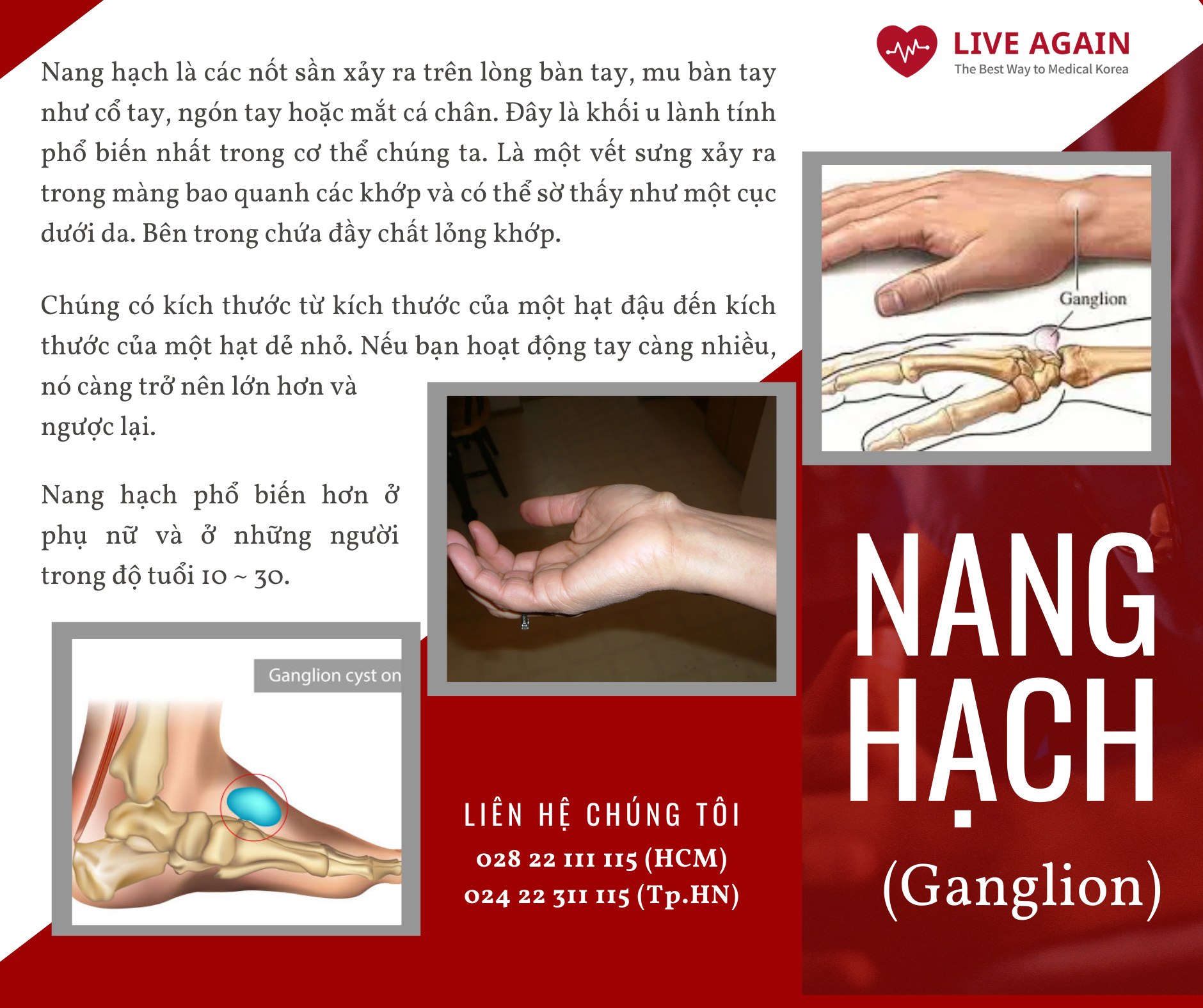
- What is flu?
Flu is an illness caused by the influenza virus, which is one of the viruses that can cause cold symptoms. It is also known as the flu. The flu differs from the common cold in that it presents with more pronounced systemic symptoms such as fever, muscle aches, and headaches, compared to localized symptoms like a runny nose, cough, and sore throat. The incidence of flu is highest from October to May, during cold and dry weather.
- Cause of flu
Persistent electron mutations in the virus lead to the emergence of antigenic variants that lack immunity, and these non-immune viruses spread rapidly between individuals, resulting in pandemics.
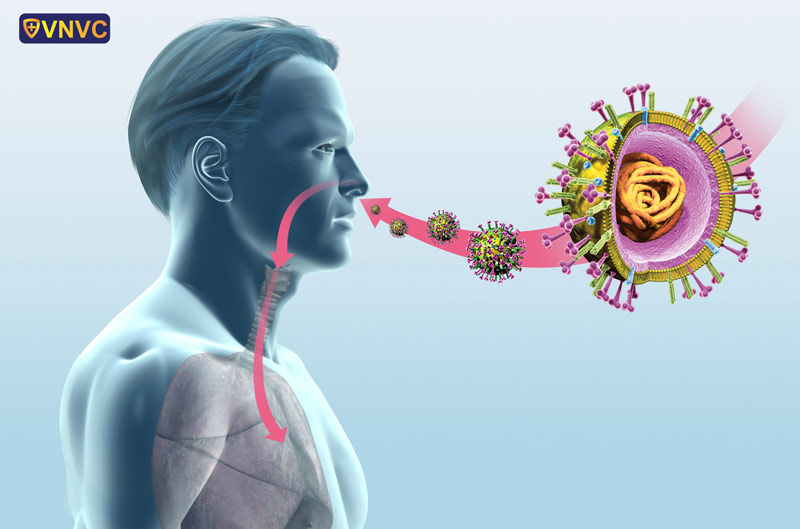
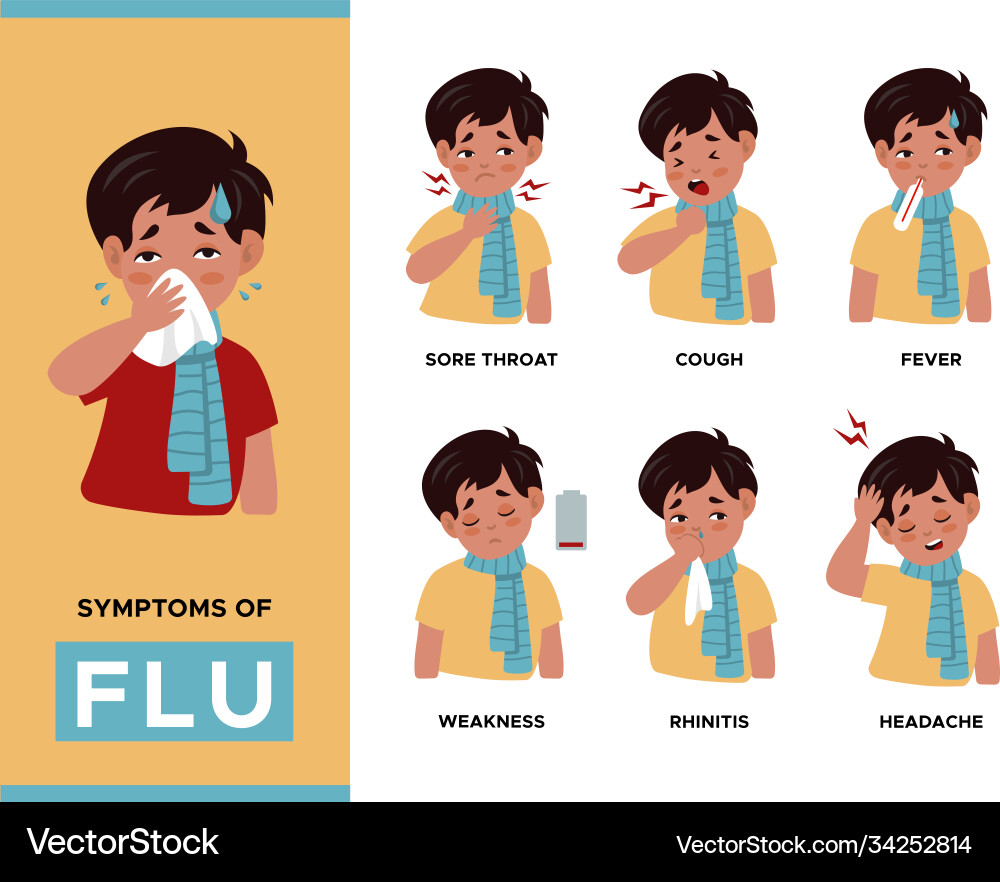
- Symptoms of flu
The symptoms of influenza are more severe than those of a common cold. High fever accompanied by fatigue leads to intense headaches, chills, and muscle aches. Symptoms such as sore throat, cough, and runny nose also occur alongside systemic symptoms.
If a healthy adult experiences a very severe cold with symptoms so intense that they need to take 2 to 3 days off work, it is highly likely that they have influenza.
In children, symptoms often include excessive drooling, loss of appetite, irritability, and difficulty sleeping. Digestive symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain frequently appear, and sometimes seizures can occur due to fever.
- Diagnosis of influenza
Depending on the level of influenza outbreaks in the community, symptoms similar to influenza (influenza-like illness, fever + cough or sore throat) can be diagnosed clinically. In some cases, the diagnosis is confirmed by rapid antigen tests, RT-PCR testing, and throat culture tests.
- Treat flu
To treat influenza, it is crucial to get plenty of rest and sleep. Patients at high risk for complications should be given antiviral medications such as oseltamivir and zanamivir as soon as possible. Even if they do not belong to a high-risk group, if complications or severe symptoms arise, antiviral medications should still be administered promptly. Aspirin is contraindicated in children under 18 years of age as it may lead to Reye’s syndrome.
- Monitor and note flu
Patients typically experience fever and systemic symptoms for 2 to 3 days, followed by recovery. Most symptoms improve after about a week, although cough may persist for several weeks. Pneumonia is the most common complication, especially in immunocompromised individuals, children, and the elderly with chronic pulmonary heart disease, which can be fatal.
If infected with influenza, symptoms usually improve within a week, and the virus is not contagious after that. Therefore, influenza patients should limit their outings when possible and should wear masks during the illness.
Annual influenza vaccination is recommended before the flu season, ideally between September and November. It takes about 2 weeks to develop protective antibodies after vaccination.
Priority groups for the influenza vaccine include adults over 50, individuals with underlying conditions such as chronic lung disease, heart disease, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, chronic liver disease, malignancies, immunocompromised patients, children aged 6 to 18 who are taking aspirin, individuals receiving treatment or rehabilitation in congregate settings such as social welfare facilities and nursing homes, as well as healthcare workers. However, new influenza strains are more easily contracted by younger individuals, so all children over 6 months and adults should receive the influenza vaccine.