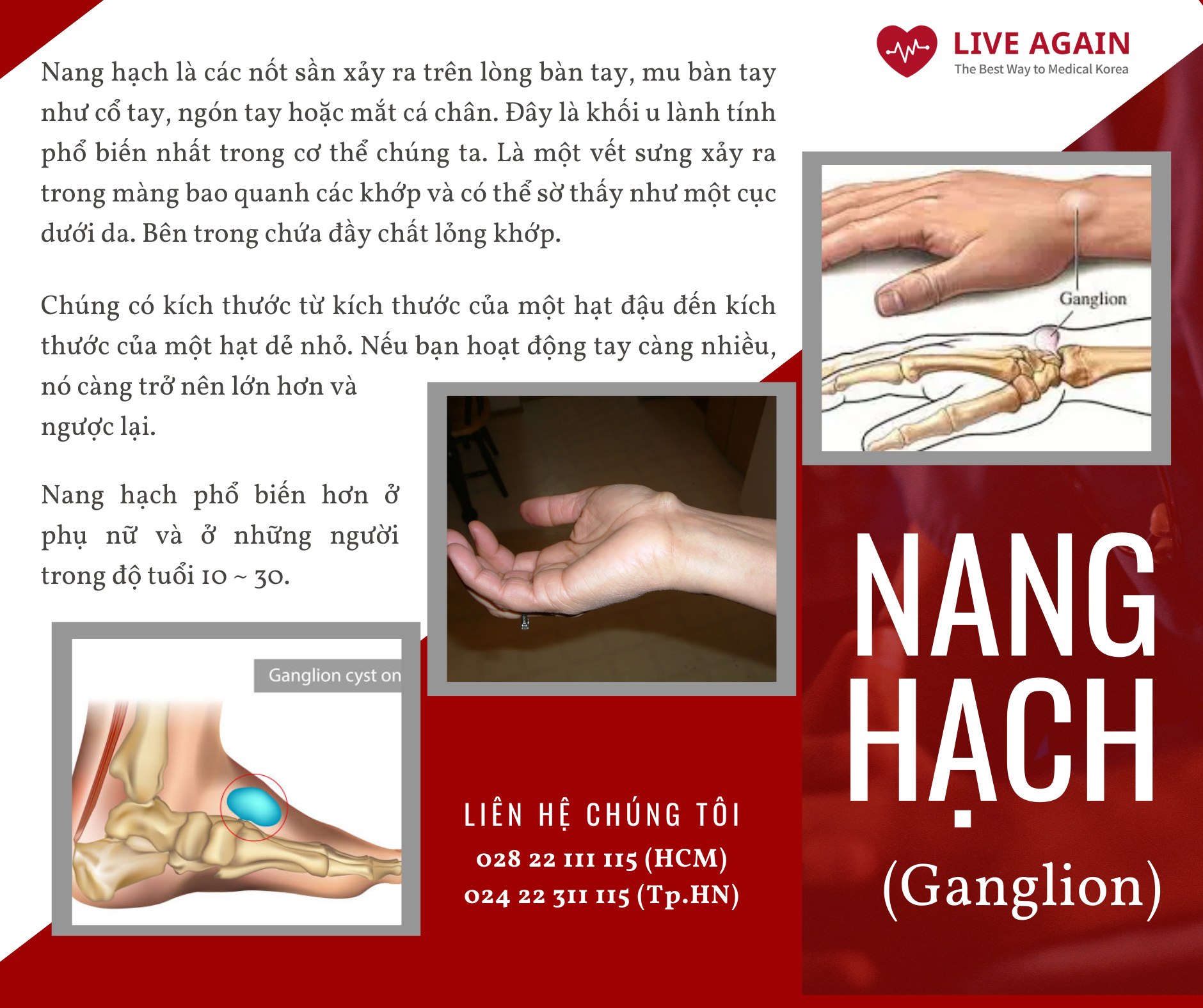
- What is a non-self- healing fracture?
Union is the bonding of bone after a fracture. Malunion refers to the bone not being aligned correctly during healing. Nonunion is the condition where the healing process of the fracture is not observed, and the bone remains unhealed. In cases of nonunion, the fracture line may still be visible or hardening may be confirmed at the site of the fracture.
Additionally, there may be no bone formation at all. Pseudoarthrosis is a bone tissue that often forms during the healing process after a fracture, and when the bones are bonded together, it becomes normal bone. The process of bone union does not occur naturally; it requires orthopedic interventions such as bone grafting or corrective surgery.
- Causes of non-self-healing bone fractures
(1) Risk factors for bone fractures
Risk factors for fractures include age, nutritional status, smoking, chronic alcoholism, infection at the surgical site, diabetes, hemiplegia, and open fractures.
(2) Causes of Malunion
Malunion can occur when the bone is not properly aligned, when the fractured area is not well stabilized, when there is significant soft tissue damage, or when the central nervous system is injured, leading to spastic paralysis.
(3) Causes of Nonunion
Nonunion can occur when there is severe soft tissue damage during the fracture, inadequate blood supply to the fracture site, infection or bone disease, intra-articular fractures, significant bone fragmentation where the necessary fragments for healing are missing, or when the fracture site continues to move.
- Symptoms of bone fractures that do not heal on their own
(1) Symptoms of Malunion
Malunion occurs when a fractured bone heals, but not in the correct position, resulting in angular deformity and rotational malalignment. This can lead to aesthetic issues and functional disorders. Malunion at a joint surface can result in significant disability.
(2) Nonunion symptoms
- Diagnosis of non-healing bone fractures
Symptoms of malunion or nonunion after a fracture can be identified through X-rays, CT scans, and blood tests may also be conducted to check for inflammation.
- Treatment of non-healing bone fractures
(1) Malunion treatment
Treatment should be determined based on the fracture area and the degree of deformity. If the damaged area causes abnormalities in daily activities, corrective osteotomy may be performed. Corrective osteotomy is a procedure in which the bone is re-fractured to adjust the angle or rotational deformity and then stabilized with metal. For about 2 to 3 months post-surgery, a cast or brace will be necessary. Additionally, you will need to undergo rehabilitation physical therapy. Post-operative treatment guidelines may vary depending on the surgical method or the patient’s condition.
(2) Nonunion treatment
The goal of treating nonunion is to eliminate pain, restore alignment through bone consolidation, and rehabilitate the injured limb. Treatment methods can be divided into non-surgical and surgical approaches. It is important to choose a treatment method that is appropriate for each patient.
– Non-surgical methods: casting and orthotics, electrical stimulation, ultrasound, bone marrow injection.
– Surgical methods: debridement, autograft, scaffold expansion, free vascularized bone graft, allograft, bone substitute, metal plate fixation, intramedullary fixation, external fixation device.