- What is RSV virus infection?
RSV infection is a contagious respiratory illness caused by the RSV virus, also known as respiratory syncytial virus. It is highly contagious, with nearly all children being infected by the age of 2.
Once infected with this virus, patients can be reinfected throughout their lives. In adults, the illness typically presents with mild cold symptoms; however, those who are immunocompromised or elderly may experience severe infections.
Children aged 3 months to under 5 years have the highest hospitalization rates following infection. RSV primarily causes bronchiolitis and pneumonia, with a high risk of mortality in young children infected with the virus.
High-risk infants, such as premature babies, children with chronic lung disease, or those with congenital heart disease, may experience serious complications from RSV infection.
RSV infections commonly occur from fall to early spring but can sometimes appear at any time of the year. The infection rate is particularly high in crowded environments such as playgrounds.
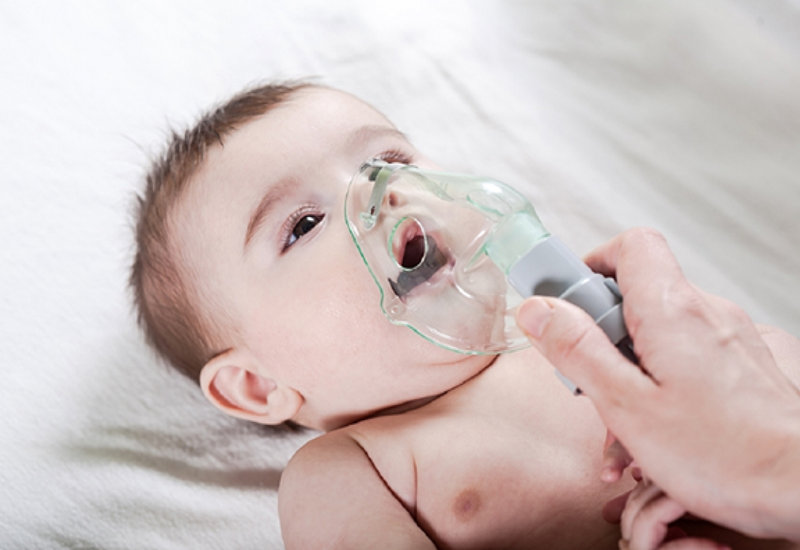
- Cause of RSV virus infection
The RSV virus is very commonly encountered in daily life and can survive for hours on surfaces such as kitchen countertops, toys, towels, blankets, used tissues, and other objects. If you come into contact with these RSV viruses, you are likely to become infected. Young children living with many family members or attending daycare are at a higher risk of infection.
- Symptoms of RSV virus infection
The incubation period for RSV infection is 2 to 8 days, and symptoms resemble those of a common cold, including sneezing, nasal congestion, runny nose, sore throat, and fever. However, it can progress to more severe symptoms such as wheezing, rapid breathing, severe coughing, difficulty breathing, cyanosis (bluish or gray skin), and challenges with eating, drinking, and sleeping.

- Diagnosis of RSV virus infection
The diagnosis of RSV infection can be made through sputum culture testing. If differential diagnosis does not reveal bacterial pneumonia or other upper respiratory tract viruses such as rhinovirus or bronchiolitis, it is important to consider the possibility that the child has been infected with RSV.
If there is an occurrence of non-infectious hypoxia, pneumonia, or asthma due to aspiration of foreign objects, differential diagnosis should be conducted.
- Treatment of RSV virus infection
In the treatment of RSV infection, there is no preventive vaccine or antiviral medication available, so conservative treatment based on symptoms is the top priority. For infants, Ribavirin may be administered via inhalation.
Additionally, for high-risk groups such as children with bronchopulmonary dysplasia or congenital heart disease, RSV immune globulin can be injected during the winter to prevent infection, or monthly intramuscular injections of targeted monoclonal anti-RSV antibodies can be given from September to March when RSV is spreading rapidly.
- Monitor and take note of this virus
Infants hospitalized due to RSV infection are monitored and found to have a higher incidence of asthma or abnormal lung function after 10 years. The mortality rate from lower respiratory infections is approximately 2%.
The risk of death may increase due to symptoms related to neurological, cardiac, pulmonary, or immune disorders. The younger the child, the higher the risk of mortality from bronchiolitis caused by RSV. RSV is the leading cause of death in infants under 1 year old. The annual mortality rate per 100,000 infants under 1 year is about 1.3 to 2.5 times higher than that from influenza.