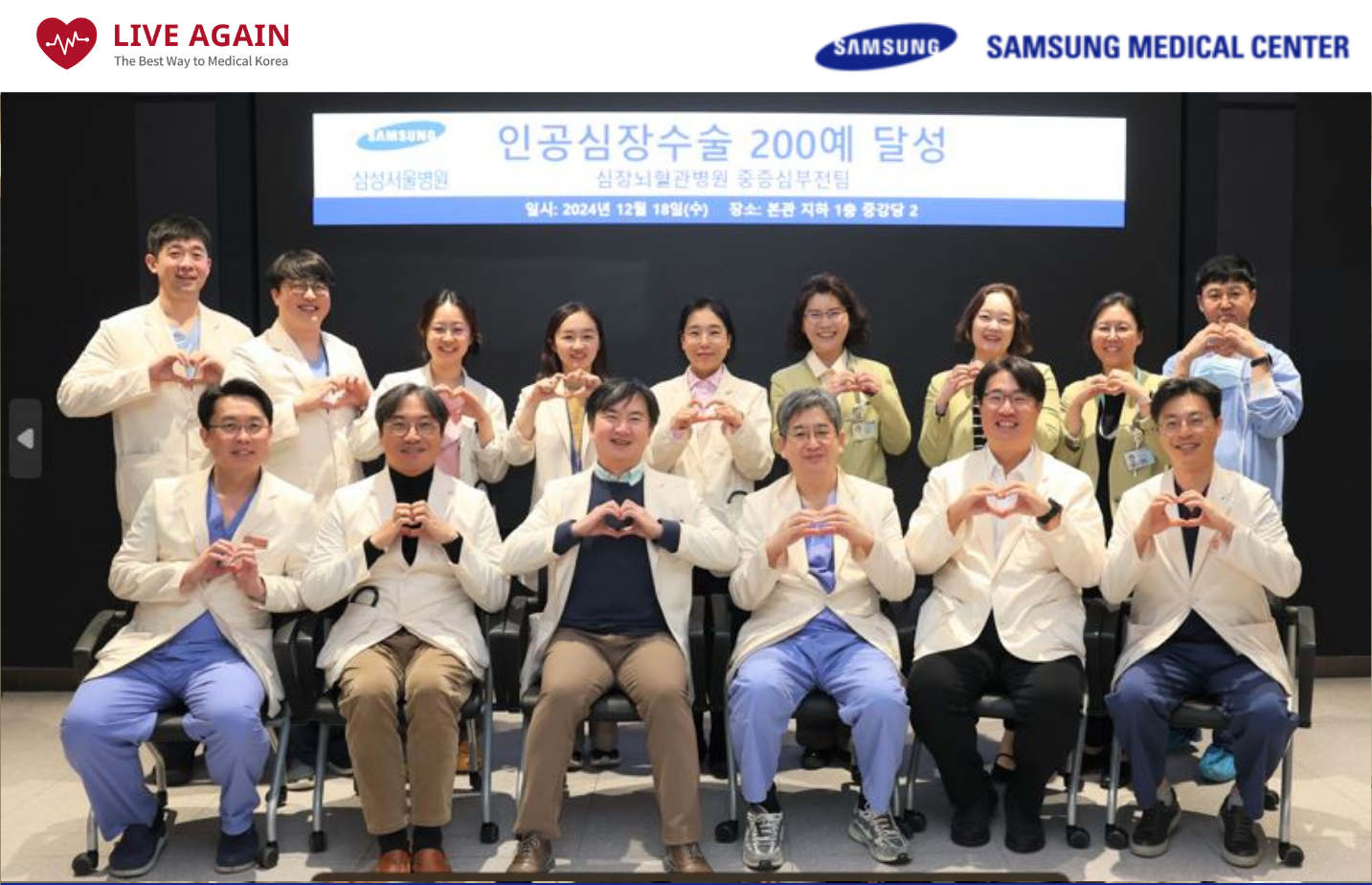
Why Transplantation in Korea
- Korea Has Established a Systematic Foundation
As the Act on Organ Donation was enacted and the KONOS (Korean Network for Organ Sharing) was founded in 2000, the government level support and management of organ transplantation commenced. In response to the needs of an independent institution for securing more organ donation from deceased donors, KODA (Korea Organ Donation Agency) was founded in 2009 to promote and facilitate the donation of organs from brain death patients and control thereof.
- Growth of Organ Transplantation in Korea
Since the year 2000, organ transplantation cases were carried out nationwide, organ transplantation in Korea has been growing steadily.
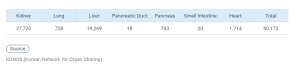
- Status of Living Organ Donor in Korea
Korea has the highest number of living donors per million people in any of the Asia-Pacific contries and ranks 2nd in terms of the number of living donors per million people worldwide (IRODaT 2019).
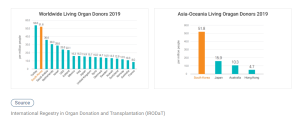
- The Largest Living Donor Organ Transplantation Program in the World
Since the first LDLT (living donor liver transplantation) in Korea was performed in 1997, LDLT in Korea has been growing steadily. Currently, Korea is the world’s No. 1 country in the LDLT field, with the highest annual number of transplantation surgeries in the world. 22.9 patients out of million people in Korea receive living donor liver transplantation surgery, which is the largest number in the world. Such number is over 10 times bigger than that in Japan and Hong Kong where liver transplantation is more generally carried out than any other World countries (IRODaT 2019). Since the first LDKT (living donor kidney transplantation) in Korea was performed in 1969, LDKT in Korea has been continuously growing. In 2019, Korea records the largest number of LDKT in Asia-Pacific countries and ranks 4th in terms of the number of LDKT per million people worldwide (IRODaT 2019).
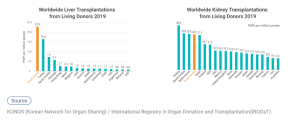
- Excellent Outcomes of Living Donor Organ Transplantation in Korea
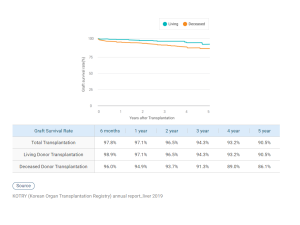
Successful Rate of LDLT(Living Donor Liver Transplantation)
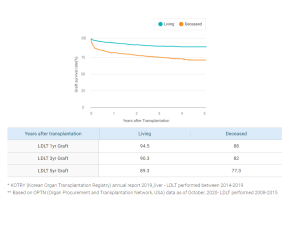
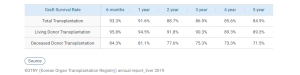
Successful Rate of LDLT(Living Donor Liver Transplantation)
Advanced Treatment
- Innovations of Liver and Kidney Transplantation in Korea
Korea has developed many innovative new surgical techniques which has now become the standard technique in most centers around the world. Since the introduction of desensitization therapy that can remove anti-ABO antibodies prior to transplantation in 2007, Korea has been performing incompatible blood type LT and KT transplantation successfully. As of the end of 2019, a total of 11,682 cases of incompatible blood type LDLT have been successfully completed. Since Feb. 2007, more than 2,501 cases of ABO-incompatible LDKT were performed until 2019. ABO-incompatible LDKT is rapidly increasing.
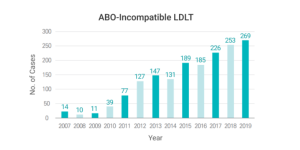
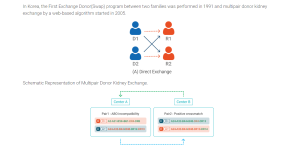
- Innovations in living donor liver transplantation in Korea
Korea, which holds the dominant position in the world’s living donor transplantation, has been developing a wide range of surgical technologies related to liver transplantation and a number of such technologies are generally used worldwide in these days.
Case of Cutting Edge Equipments for Transplantation
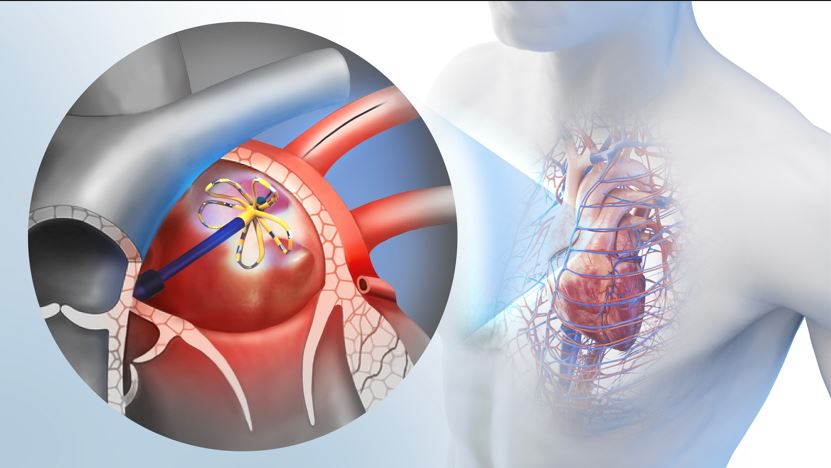
Robotic surgery is also being performed on organ transplantation in Korea. The surgical area can be viewed in detail with 10-fold magnified stereoscopic images, and scars can be minimized with minimal incision due to robotic surgery.
Case of Transplantation in Korea
Korea has performed the world’s first ‘2:1 living donor liver transplantation’.
Although the surgical process is much more complicated than conventional one-on-one living donor liver transplantation, the success rate and survival rate of 2:1 living donor liver transplantation are comparable to that of conventional one-on-one living donor liver transplantation. Even if the blood type is different, Korean medical staff can perform successful liver transplant surgery even in liver cancer, which has highly recurrence rate.